Radarcape:Firmware Versions: Difference between revisions
imported>Dl4mea |
imported>Dl4mea |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
* Planeplotter aircraft sharing added | * Planeplotter aircraft sharing added | ||
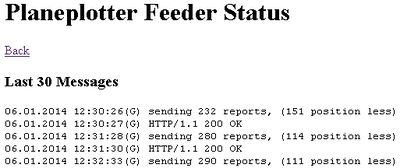
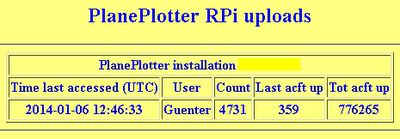
This is the first release which publishes the current | This is the first release which publishes the current known aircraft to the Planeplotter network. Uploading can be enabled and disabled. You need to get a sharing authorisation, whichis explained in the configuration dialogue. There is also a status page and a link provided to the Planeplotter server which shows your past uploads. Uploading is currently done once every minute plus a random 0...14 sec. (The uploading methode was prepared for R-Pi, Bev needs to rename the service now.) | ||
MLAT support will be added as soon as possible. | MLAT support will be added as soon as possible. | ||
Revision as of 15:37, 6 January 2014
Software Packages
Starting with November 2013, the release strategy will be Linux installer packages, which include the Linux software as well as the FPGA firmware.
Known issues of latest Release
- The Google Earth KML does not open automatically from the browser on all all machines.
- Web page and KML refresh times do not apply when beeing changed while the display is running: You need to reload the page in order to apply changes.
- Linux time does not run correct but delay about 85sec every 15min. It however is corrected by connmand NTP.
- If operated without GPS, the unit must be switched to legacy 12MHz timestmap manually. Also, the functionality in some items may be undefined without GPS.
Release_140106.13.29 - Planeplotter Feeder, Ground Decoding
New Features:
- Planeplotter aircraft sharing added
This is the first release which publishes the current known aircraft to the Planeplotter network. Uploading can be enabled and disabled. You need to get a sharing authorisation, whichis explained in the configuration dialogue. There is also a status page and a link provided to the Planeplotter server which shows your past uploads. Uploading is currently done once every minute plus a random 0...14 sec. (The uploading methode was prepared for R-Pi, Bev needs to rename the service now.)
MLAT support will be added as soon as possible.
- Ground decoding
Ground data is decoded. It is output in all services.
Changes:
- The Flightradar24 Feeder can now be started based on the internal deltaDB methode or Port 30003 data, as some users felt that if based on Port 30003 the acceptance rate at FR24 is higher than based on deltaDB. Please note that Port 30003 is a very inefficient protocol and consumes more CPU resources than deltaDB.
- The feeders now start only if the GPS time is available. Timestamps on web status pages contain an (X) if unknown time source, (C) if the CPU time is used and (G) if GPS time is present.
- Port 30003 output data contains GPS timestamp if available.
Install command:
opkg install -V http://www.modesbeast.com/resources/radarcaped-140106.13.29.opk
after the installation has completed
reboot
Release 131225.18.56
New Features:
- Remote control of FPGA configuration ("DIP switches") can be enabled and disabled in configuration
Solves:
- Timestamp problem: All timestamps are based on the GPS time. If not available CPU time is used
Install command:
opkg install -V http://www.modesbeast.com/resources/radarcaped-131225.18.56.opk
Release 131206.22.40
New Features:
- 2D map automatically centers on your GPS position and zooms according to your current largest distance.
Solves:
- Internet Explorer may not be display the web pages at all, Mozilla Firefox seems to be tolerant. Radarcape currently does not send the correct HTML header.
Install command:
opkg install -V http://www.modesbeast.com/resources/radarcaped-131206.22.40.opk
Release 131202.20.55
New Features:
Solves:
- KML starter did not access KML output -> Google Earth 3D view did not work
Install command:
opkg install -V http://www.modesbeast.com/resources/radarcaped-131202.20.55.opk
Release 131128.21.18: Introduction of 2D Maps
New Features:
- 2D map display on web browser
Solves:
Install command:
opkg install -V http://www.modesbeast.com/resources/radarcaped-131128.21.18.opk
Release 131127.05.01: Solves P30003 message type problem
New Features:
- none
Solves:
- The port 30003 messages MSG,2 and MSG,3 seem to be swapped. ==> actually all Port 30003 messsages were one count too low.
Install command:
opkg install -V http://www.modesbeast.com/resources/radarcaped-131127.05.01.opk
Release 131126.19.46: Configuration Page Issues Solved
New Features:
- none
Solves:
- The configuration page when beeing saved does not confirm change but show an empty page or a failure message. However the changes appear to be taken. It only happens on a few installations. Investigation is in progress.
- There was a delay when connecting to a TCP port, which is now avoided.
- HTML 'Back' link moved to the top of all pages
- Timestamp behaviour in P30003: Is now truely message generation and message capture time.
- uses GCC 4.3.3 and Boost 1.53.0
Install command:
opkg install -V http://www.modesbeast.com/resources/radarcaped-131126.19.46.opk
FPGA Firmware
Firmware update on the Radarcape is absolutely simple: Just mount the Radarcape as a drive into your Windows, then replace the existing meaADSB.rbf file with the one downloaded from this web page. You may save the existing one, but the history also exists here for download (including the version name in the file name).
The GPS timestamp
The GPS timestamp is completely handled in the FPGA (hardware) and does not require any interactions on the Linux side. This is essential to meet the required accuracy. The local clock in the FPGA (64MHz or 96MHz) is stretched or compressed to meet 1e9 counts in between two pulses by a linear algorithm, in order to avoid bigger jumps in the timestamp. Rollover from 999999999 to 0 occurs synchronously to the 1PPS leading edge. In parallel, the Second-of-Day information is read from the TSIP serial data stream and also aligned to the 1PPS pulse. Both parts are then mapped into the 48bits that are available for the timestamp and transmitted with each Mode-S or Mode-A/C message.
- SecondsOfDay are using the upper 18 bits of the timestamp
- Nanoseconds are using the lower 30 bits. The value there directly converts into a 1ns based value and does not need to be converted by sample rate
nanosec = (msg[2] & 0x3f) << 24
| msg[3] << 16
| msg[4] << 8
| msg[5];
daysec = msg[0] << 10
| msg[1] << 2
| msg[2] >> 6;
if (daysec_tm1!=daysec)
{
daysec_tm1 = daysec;
hh = (daysec/3600) % 24;
mm = (daysec/60) % 60;
ss = daysec % 60;
}
The legacy 48bit and 12MHz based timestamp however is not synchronized to 12MHz at all, so it still works as it has been since ever.
Linux and FPGA firmware package ppsjump-021 (23. Aug. 2013)
Corrections
- For enhanced stability, this version is based on Linux 3.8.
- The GPS tool is now included into the radarcape deamon. It also provides a GPS status through the web server, accessing gps.html on the integrated webserver
- The TCP ports for data streaming connect on each try, not each second.
Installation
For this version, it is essential that you update your SD card completly from scratch. Download the naked Linux 3.8 image (73MB) and make a SD card as described in Radarcape Linux Install/Configure. Please mind the two screenshots there in order to see how about the update procedure works like. (As some users had problems unpacking the XZ, there is a Linux 3.8 image ZIP Version (130MB) on the server, too)
When inserted and rebooted, either login through the serial port (Mini-USB on the back side) or via SSH/network (then your destination temporarily is “beaglebone”). Enter these commands, and don't forget to enter your known Radarcape ID when beeing asked from the skript:
cd
rm install38.sh
wget http://www.modesbeast.com/resources/install38.sh
sh ./install38.sh
reboot -f
FPGA Firmware meaADSB_ep3_143_ppsjump-020
Corrections
The GPS timestamp locked on multiplies of 32768 in situations when the 1PPS signal was disturbed by external matters.
superseeded by ppsjump-021
FPGA Firmware meaADSB_ep3_141_gpsmlat-3
Corrections
SecondOfDay (the upper 18 bits of the timestamp in GPS mode) and Nanoseconds (the lower 30 bits) are now synchronized.
Note that in order to overcome above problem with negative timestamps, the GPS read: absolute timestamp of Mode-S and Mode-A/C frames is taken at the end of the frame, at least until further notice. This does not make any difference for multilateration, as long as this feature is unique provided by the Radarcape.
Firmware meaADSB_ep3_141_gpsmlat-3
md5sum meaadsb_ep3_141_gpsmlat-3.rbf
86d6cdb069868e4f57d47dfc3441593c meaadsb_ep3_141_gpsmlat-3.rbf
md5sum meaadsb_ep3_141_gpsmlat-3.zip
5bcae05ea429b4ef943b303314e22b82 meaadsb_ep3_141_gpsmlat-3.zip
FPGA Firmware meaADSB_ep3_141_gpsmlat-2
Firmware meaADSB_ep3_141_gpsmlat-2 has a working GPS timestamp function. Therefore, DIP#5 switch selects either the standard 12MHz timestamp (when off) or the GPS timestamp (when on).
md5sum meaADSB_ep3_141_gpsmlat-2.rbf
dc7a6278a668b1bdb81fd67e7a1891a6 meaADSB_ep3_141_gpsmlat-2.rbf
md5sum meaADSB_ep3_141_gpsmlat-2.zip
ba54740894406cb38e8dd95d0fc3e3e8 meaADSB_ep3_141_gpsmlat-2.zip
| Radarcape DIP Switch | DIP#1 | DIP#2 | DIP#3 | DIP#4 | DIP#5 | DIP#6 | DIP#7 | DIP#8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equivalent Beast DIP with resp. to PP setting |
DIP#3 | DIP#4 | DIP#5 | DIP#6 | DIP#7 | DIP#8 | DIP#9 | DIP#10 |
| When ON | Binary format | only DF-11 and DF-17 |
enable MLAT in AVR format |
CRC check disabled |
GPS based timestamp |
RTS hardware handshake |
1 Bit FEC disabled |
Mode-A/C decoding enabled |
| When OFF | AVR format | all usable DF | no MLAT in AVR format |
CRC check enabled |
standard 12MHz timestamp |
hardware hand- shake disabled |
1 Bit FEC enabled |
Mode-A/C decoding disabled |
| Command Character |
c/C | d/D | e/E | f/F | g/G | h/H | i/I | j/J |
| not used in binary format |
An upper case character is equal to a DIP that is in ON position, a lower case character equal to DIP in open position
The green LED next to the SMA connector is used as GPS indicator:
- Short on, long off: Just 1PPS is present, but no time of day information
- On and off time equal: 1PPS present, Time of day present, but there is a synchronisation offset
- Long on, short off: 1PPS present, Time of day present, Internal time is synchronized to GPS
It is not a problem if the clock sometimes falls back from (3) to (2), because the sensitivity of synchronisation check is +/-1 tick.
The center red LED flashes as an indication of operating about twice per second. It should flash very fast in case that hardware handshake is active.
The GPS based timestamp still uses the standard 48 bits as known from the 12MHz timestamp, but in different way:
- the lower 30 bits are the time since the last 1PPS pulse, in 1ns steps, currently 15ns resolution
- the upper 18 bits are the Seconds-Of-Day, starting with zero at midnight UTC
Known Issues (meaADSB_ep3_141_gpsmlat-2)
- Within the GPS timestamp, the Second-Of-Day part advances in the mid of the 0-999999999ns phase ⇒ next version
- Sometimes the Second-Of-Day part does not increment at the rollover of the nanosecond part ⇒ next version
- The absolute value of the GPS timestamp of 14 bytes long Mode-S frames is offset, however since all units do have that error, it is not a big problem for multilateration ⇒ wait for release
- Negative delta time offsets between consequent frames ⇒ not an issue (see below)
Negative delta time between consequent frames
If you look at the block diagram of the Mode-S Beast, recognize that there are several frame decoders working in parallel, plus the Mode-A/C decoder, which is not yet mentioned in the picture. They all work independently, their output - a ready frame - is written into a FIFO in order to buffer it for RS232 transmission.
It now may happen that during the reception of a Mode-S frame, an overlapping Mode-AC frame becomes decoded in parallel and is written into the FIFO, prior to the end of the Mode-S frame. Since the timestamps are taken at the start of frame, in that situation, the Mode-AC frame with a later timestamp is written to the FIFO before the Mode-S frame finishes. Consequentally on the output, the later timestamp of the Mode-S frame appears ahead of the Mode-S frame's.
It is easy to understand with the Mode-AC as a cause, but the same happens if one of the noise decoders or the overlapping Mode-S frame decoder outputs a frame while the other is still working.
Sorting that in the FPGA would cost too many ressources, so users of the timestamps anyway need a matching algorithm among different units, so that algorithm should be aware about this situation.
If you think about swapping them around, note that it may not happen with two frames but several, e.g. in the situation that two Mode-A/C frames do overlap a 14 byte Mode-S frame.