Radarcape:Installation Guide: Difference between revisions
imported>Beastadmin No edit summary |
imported>Beastadmin No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{| | {| | ||
|[[File:Beginner.png|For Beginners]] | |[[File:Beginner.png|For Beginners]] | ||
|'' | |''Required computer skills to execute these tasks: Beginner'' | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 19:10, 25 March 2015

|
Required computer skills to execute these tasks: Beginner |
Connect Radarcape Hardware
Plug the following connectors into the Radarcape
- Mode-S antenna
- GPS antenna
- Ethernet/LAN cable
- Power cable
Connect the power supply with the electrical outlet.
Antenna placement
Mode-S Antenna
The Mode-S antenna should be placed as free and as high as possible.
GPS Antenna
The GPS antenna should be placed to a point with at least half of the sky in free sight, for example a window sill.
Some users reported running the GPS antenna indoors. This is not guaranteed to work.
Software Configuration
The Radarcape as a network device - the hostname or DNS name
Network devices can be accessed in two ways:
- via IP address (e.g., 192.168.1.157)
- via hostname (e.g., radarcape)
The IP address is provided to your Radarcape either during startup via the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) service or a fixed address can be set on the device. Automatic configuration via DHCP is the default configuration of the Radarcape. Usually, your internet router provides the DHCP service in your network and assignes an IP address to your device. Fixed addresses can be assigned configured via the Linux command line. For the configuration of a fixed IP address, please refer to one of the Linux manuals you can find in the Internet.
The hostname is a given name that is stored internally in your device (see /etc/hostname). If there is no label on the back side of your Radarcape, the hostname is either radarcape.
Most internet routers provide the DHCP and Domain Name System (DNS) services for local network devices. The DHCP service automatically asignes IP adresses in local networks. DNS is used by clients (e.g., your browser) to resolve host names to IP addresses. During the boot sequence, the radarcape requests an IP address from this DHCP service. It also reports it's hostname to the DHCP service on the router. At this stage, most routers automatically update their DNS database with the hostname and the IP address of your radarcape. This is strongly required if you want to access your Radarcape via the hostname.
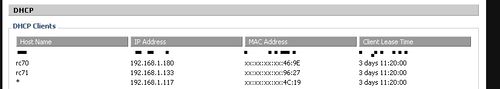
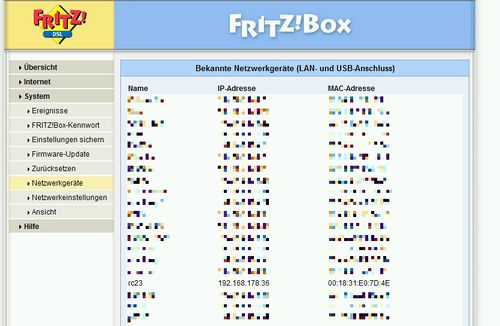
If you are not able to access your Radarcape via the hostname, usually the DNS service has not been updated. Some internet routers do not support this feature. In this case you can access the Radarcape via it's IP address. To obtain the IP address, open the Web interface of your internet router. Usually, it will contain a page that lists all IP addresses that were assigned by the DHCP service.
This is how you identify your device in the network. Take care on an probable issue with Windows, described here Radarcape:ConnectivityFailures
We will develop a Radarcape finder pretty soon, so you don't have do obtain it in this manual ways.
 |
 |
Software Configuration
The Radarcape configuration can be modified via the Web interface.
Basestation and Flightroute Databases
The Radarcape can use external databases for displaying additional information to the 2D map and the aircraft list.
- basestation.sqb: aircraft type and registration.
- flightroutes.sqb: flightplan information (origin and destination)
These databases are not installed when we ship the Radarcape. Users can download and install them from third-party sources. This can be done via the Software Maintenance menu.
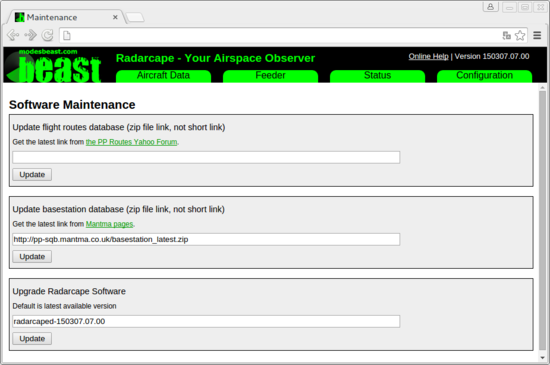
The databases can be obtained from these sources:
- Plane Base NG (basestation.sqb)
- PP Routes Yahoo Group (flightroutes.sqb, registration required)
As both databases contain information that is subject to change, we recommend you to update these databases in regular intervals.
Settings Web Page
Various configuration settings can be made on the Settings menu.
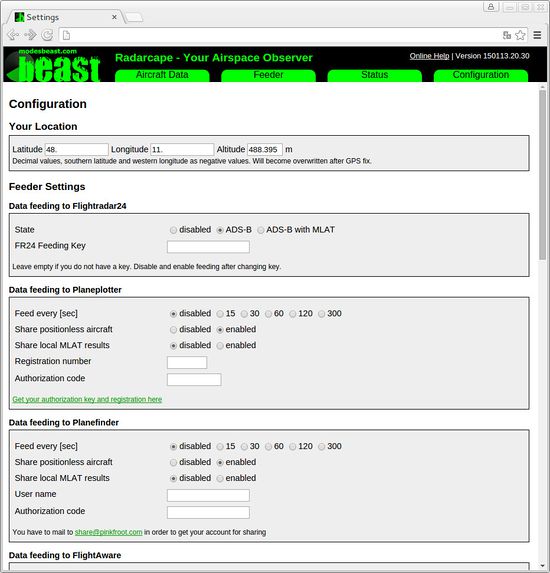
The settings menu also provides the posibility to configure and enable Mode-S feeding to the following services:
- Flightradar 24
- Planeplotter
- Planefinder
- Flightaware
Feeding credentials must be obtained from these service provides.
Advanced Configuration Interfaces / Commandline Access
There are two ways how to connect to the Linux system:
- SSH through the network
- Back side Mini USB connector
Set Root Password
In the default configuration, no password is set for the root user (administrator) on the Radarcape. We strongly advise you to set a password for security reasons.
Please remember your password as there is currently no other password recovery method than creating a new SD card image for your Radarcape.
First you must login to your Radarcape via SSH.
- Windows users can use the free SSH client Putty.
- Linux/Unix users may use SSH from the command line.
ssh root@radarcape
An initial root password has not been set. Therefore, you can login with user root and no password.
After you have logged in on your Radarcape, you can set a new root password with the following command:
passwd
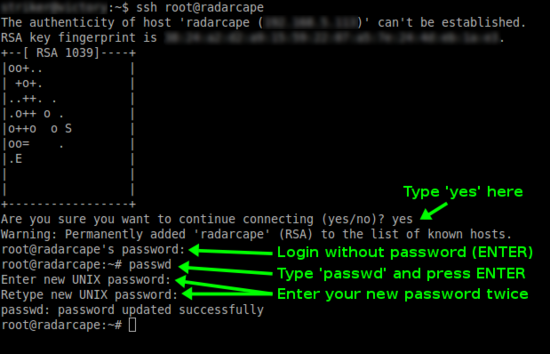
The message passwd: password updated successfully will indicate that the new password has been set.
