Radarcape:Installation Guide: Difference between revisions
imported>Dl4mea |
imported>Dl4mea |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
* IP address, something like 192.168.1.157 | * IP address, something like 192.168.1.157 | ||
The '''IP address''' is given to your device during startup from either a DHPC server or from predefined fixed settings. Mostly your DSL or internet router is also working as DHCP. You can look into your router's user interface, IP list, in order to obtain the Radarcape's IP address. Mind that the IP address is only unique in your network segment. If behind a firewall or router, your devices might be summarized under one common and different IP address. That is when port mapping plays a role. | The '''IP address''' is given to your device during startup from either a DHPC server or from predefined fixed settings. Mostly your DSL or internet router is also working as DHCP. You can look into your router's user interface, IP list, in order to obtain the Radarcape's IP address. Mind that the IP address is only unique in your network segment. If behind a firewall or router, your devices might be summarized under one common and different IP address. That is when port mapping plays a role.<br \>Fixed IP addresses are currently only available by reconfiguring the Linux, you will find plenty of information here in the internet. Mind that the Radarcape normally runs with Linux 3.8 or later. | ||
The '''hostname''' is a given name internally in your device. | The '''hostname''' is a given name internally in your device (it is located in the file /etc/hostname). During the process of getting the IP address, the devices tells the DHCP server its name. If there is no label on the back side of your Radarcape, the hostname is always '''''radarcape'''''. Other names might be '''''rc<nn>''''', with <nn> beeing a number. | ||
This is how you identify your device in the network. | This is how you identify your device in the network. Take care on an probable issue with Windows, described here [[Radarcape:ConnectivityFailures]] | ||
We will develop a Radarcape finder pretty soon. | We will develop a Radarcape finder pretty soon, so you don't have do obtain it in this manual ways. | ||
==Configuration Interfaces== | ==Configuration Interfaces== | ||
Revision as of 05:58, 15 November 2013

|
The tasks described in this manual require little to medium Unix/Linux experience. |
Connect Radarcape Hardware
Plug the following connectors into the Radarcape
- Mode-S antenna
- GPS antenna
- Ethernet/LAN cable
- Power cable
Connect the power supply with the electrical outlet.
Software Configuration
Some words about the Radarcape as a network device - the HOSTNAME
In an network environment there are basically two ways how to identify a device
- hostname, which is a text string, a given name
- IP address, something like 192.168.1.157
The IP address is given to your device during startup from either a DHPC server or from predefined fixed settings. Mostly your DSL or internet router is also working as DHCP. You can look into your router's user interface, IP list, in order to obtain the Radarcape's IP address. Mind that the IP address is only unique in your network segment. If behind a firewall or router, your devices might be summarized under one common and different IP address. That is when port mapping plays a role.
Fixed IP addresses are currently only available by reconfiguring the Linux, you will find plenty of information here in the internet. Mind that the Radarcape normally runs with Linux 3.8 or later.
The hostname is a given name internally in your device (it is located in the file /etc/hostname). During the process of getting the IP address, the devices tells the DHCP server its name. If there is no label on the back side of your Radarcape, the hostname is always radarcape. Other names might be rc<nn>, with <nn> beeing a number.
This is how you identify your device in the network. Take care on an probable issue with Windows, described here Radarcape:ConnectivityFailures
We will develop a Radarcape finder pretty soon, so you don't have do obtain it in this manual ways.
Configuration Interfaces
Basi
Get DNS Name and IP Address of the Radarcape
The Radarcape obtains its IP address via DHCP. Usually, the Internet router provides DHCP services in small networks (e.g., home network) and a list of distributed IP addresses can be obtained via its web interface.
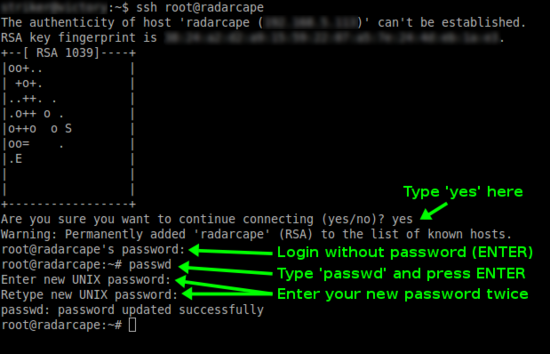
Set Root Password
In the default configuration, no password is set for the root user (administrator) on the Radarcape. We strongly advise you to set a password for security reasons. Please remind your password as there is currently no other password recovery method than creating a new SD card image for your Radarcape.
First you must login to your Radarcape via SSH.
- Windows users can use the free SSH client Putty.
- Linux/Unix users may use SSH from the command line.
Please replace rs11.home with the DNS name or IP address of your personal Radarcape.
An initial root password has not been set. Therefore, you can login with user root and no password.
After you have logged in on your Radarcape, you can set a new root password with the following command:
passwd
The message passwd: password updated successfully will indicate that the new password has been set.