Radarcape:Software Features: Difference between revisions
| Line 271: | Line 271: | ||
===Data Source Identifiers=== | |||
"src", "ava" field contents | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align: left; font-size:75%;" | |||
!src | |||
!Source | |||
!Frequency | |||
|- | |||
|A | |||
|ADS-B | |||
|1090 MHz + 978 MHz | |||
|- | |||
|M | |||
|Multilateration | |||
|1090 MHz | |||
|- | |||
|L | |||
|OGN Decoder | |||
|868 MHz | |||
|- | |||
|F | |||
|piAware | |||
|1090 MHz | |||
|- | |||
|O | |||
|OGN Server Connection | |||
|868 MHz | |||
|- | |||
|S | |||
|FLARM SkyLens FLARM | |||
|868 MHz | |||
|- | |||
|D | |||
|FLARM SkyLens ADS-L | |||
|868 MHz | |||
|} | |||
===ADS-B Data Subclasses=== | ===ADS-B Data Subclasses=== | ||
Revision as of 14:28, 11 April 2024
Radarcape/Air!Squitter Software Features
The Radarcape provides output of data in several levels:
- true raw data
- decoded data on a per frame basis (e.g., port 30003)
- decoded data on summary basis (e.g., aircraftlist.json, deltadb.txt)
- web browser support (aircraft list, 2D map)
- 3D output (live KML data)
Web Based Aircraft Table
A list of received aircraft can be fetched via a build-in Web server. This list can be sorted ascending and descending in each column by simply clicking on the arrows. The distances are automatically calculated from aircraft positions and your GPS coordinates.
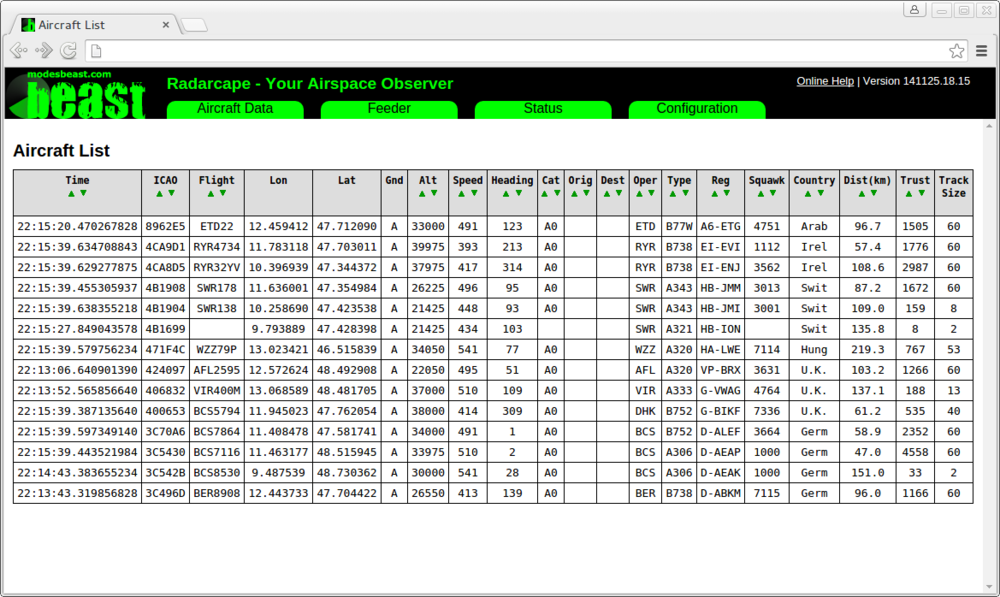
| Name | Description | Notes |
| Time (hh:mm:ss:ns) | Time of last message received from the aircraft | |
| ICAO | 24 bit ICAO hex ID unique identification of aircraft | |
| Flight | the Call Sign as it is transmitted from the aircraft itself | |
| Lon | Longitude | |
| Lat | Latitude | |
| Src | Source of Lat/Lon: A=ADSB M=MLAT | |
| GndAir | Aircraft is on ground (identified with GND bit or DF-18 messages) or airborne | |
| Alt | Altitude (feet) at 1013 mb | |
| VRate | Vertical rate in feet/min | |
| Speed | Ground Speed in knots | |
| Track | Direction that the aircraft is travelling in degrees true | |
| Cat | Cat A0..C5 are transmitted by aircraft in Mode-S messages | |
| Orig | Origin of flight | taken from database, perform Maintenance -> Update flight routes database |
| Destin | Destination of flight | taken from database, perform Maintenance -> Update flight routes database |
| Oper | Flight operator | taken from database, perform Maintenance -> Update flight routes database |
| Type | Aircraft Type | taken from database, perform Maintenance -> Update flight routes database |
| Reg | Registration of aircraft | taken from database, perform Maintenance -> Update base station database |
| Squawk | Squawk code as it is transmitted by aircraft in Mode-S messages | |
| Country | Country that the aircraft is registered for, indicated through the upper bits in the ICAO hex id | |
| Distance | Distance to the observer if its Lat, Lon is either valid by manual entry in configuration or determined by GPS | |
| Trust | Number of highly trustable DF-11 or DF-17/18 messages per aircraft. Used to desinguish ghosts, as true aircraft quickly raise this number while ghosts stay at 1 | |
| Track Size | Length of the track in 2D 3D display in 5sec sequence track points |
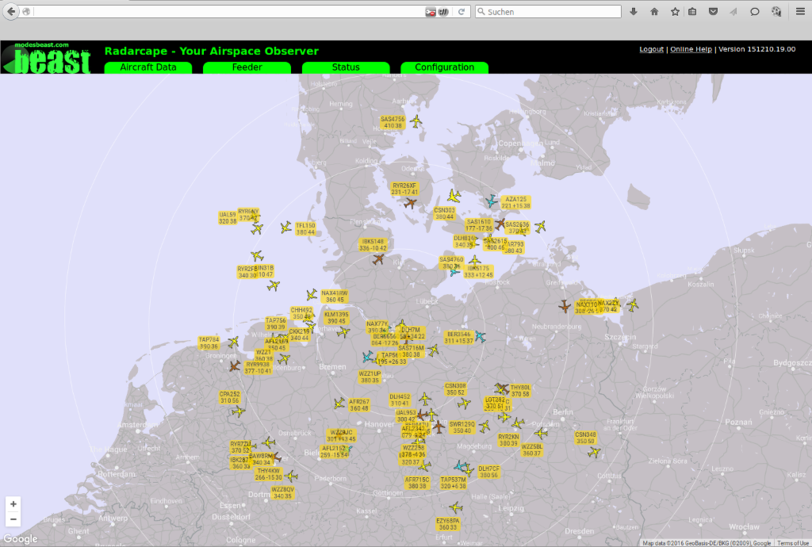
Live 2D Output
All received aircrafts with a known position are displayed on a 2D map in your Web browser.
Live 3D Output (KML/KMZ Output)
Google Earth can be attached to the Radarcape via KML/KMZ files.
An aircraft over Augsburg Airport
DeltaDB Service
The DeltaDB service can be accessed via http://radarcape/deltadb.txt. It outputs a comma separated list of all changes in the internal aircraft list since the last call or a specified time. This is an efficient replacement of port 30003 functionalities.
Aircraft List JSON Service
All data contained in the aircraft list can also be downloaded in JavaScript Object Notation (JSON). The file format can be used by other applications to access aircraft list data using the Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP) protocol.
The Aircraftlist JSON Service can be accessed via http://radarcape/aircraftlist.json.
The JSON output uses abbreviated identifiers for the data fields like below.
Note: Fields for which no data have been received might either be absent from the JSON, or set to "null". You should not expect all fields to be always available
With some additional parameters that are described in the Software Features Major 2 the list can be filtered on the server side saving some amount of data to be transferred.
| Abbreviation | Description | Minimum required ADS-B version (MOPS) |
Value Origin |
Additional Information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| uti | Time of last message: Seconds since UNIX epoch | Clock | ||
| ns | Time of last message: Nanoseconds since Second epoch | Clock | ||
| hex | ICAO Mode-S or Flarm ID, in Hex format | Mode-S or FLARM | ||
| fli | Flight Identification | Mode-S | From ADS-B or BDS2,0 as specified on ICAO Annex 10, Volume IV, Table 3-9; "?" when A/C reports loss of interface | |
| ava | Flight data: available flight data sources | One letter per available flight data sources. A=ADSB, M=Jetvision MLAT, F=FlightAware MLAT, O=OGN, L=FLARM | ||
| src | Flight data: Source | The current preferred/selected flight data source (i.o.w. for <lat>, <lon>, <alt>, <spd>, <trk> and <vrt>) | ||
| cla | ADS-B Classification | Receive Channel & ADS-B |
Subclass of ADS-B data | |
| lat | Flight data: Latitude (-90 to 90º) | <src> | ||
| lon | Flight data: Longitude (-180 to 180º) | <src> | ||
| alt | Flight data: Barometric uncalibrated altitude (ft) | <src> | ||
| spd | Flight data: Ground Speed (kt) | <src> | ||
| trk | Flight data: True track (0-360º) | <src> | ||
| vrt | Flight data: Vertical Rate (ft/min) | <src> | ||
| gda | Airborne/Ground | Mode-S | G for on ground, A for airborne (if TIS-B then lowercase g or a) | |
| cat | Aircraft category | Mode-S or FLARM | As reported in ADS-B or FLARM. See table below. | |
| org | Origin | DB | Origin airport from Flighroutes database, derived from <fli> | |
| dst | Destination | DB | Destination airport from Flighroutes database, derived from <fli> | |
| opr | Operator | DB | Operator from Basestation database, derived from <hex> | |
| typ | Type | DB | Type from Basestation database, derived from <hex> | |
| reg | Registration | DB | Registration from Basestation database with respect to <fli> or if not available automatically deduced for some countries with known mapping (FR, BE, PT, CH, US and CA) | |
| squ | Mode-A (Squawk) | Mode-S | While this is a Mode-A code, it can only be correlated in Mode-S targets. Mode-A or Mode-A/C targets are not displayed in decoded formats since they cannot be correlated with a <hex> value | |
| cou | Country | <hex> | Country according to Mode-S allocation block if decodable, mostly unusable/invalid for FLARM A/C | |
| dis | Distance (km or NM depending on configuration) | To the Receiver GNSS location | ||
| tru | Trust count | Number of Mode-S frames successfully decoded from this A/C. Statistically it's possible that for a very low count the A/C does not actually exist | ||
| dbm | Approximate signal level in dBm | |||
| lla | Age of last Position (s) | Clock | ||
| tmp | Temperature (ºC) | 0 | Mode-S | Synthetic value calculated from several fields. Might not be always reliable |
| wsp | Wind Speed (kt) | 0 | Mode-S | Synthetic value calculated from several fields. Might not be always reliable |
| wdi | Wind from Direction (0-360º) | 0 | Mode-S | Synthetic value calculated from several fields. Might not be always reliable |
| mop | ADS-B MOPS version | ADS-B | NULL=no ADS-B frames received, 0=default for unconfirmed version, 1 or 2 for corresponding confirmed version | |
| spi | SPI (Squawk ident) | Mode-S | ||
| alr | Alert status | Mode-S | 0=no alert, 1=temporary (Squawk changed previous 18s), 2=mode-s alert, 3=permanent (Squawk 7500,7600,7700). Since Mode-S DF4,5,20,21 do not distinguish between temporary and permanent alert, the value 2 is used to mean either 1 or 3 and happens for non ADS-B A/C targets | |
| ias | IAS | 0 | Mode-S | Typically not reported by a fully operational A/C as by default only Ground speed and True track are transmitted |
| tas | TAS | 0 | Mode-S | Typically not reported by a fully operational A/C as by default only Ground speed and True track are transmitted |
| hdgm | Magnetic Heading | 0 | Mode-S | Typically not reported by a fully operational A/C as by default only Ground speed and True track are transmitted |
| hdgt | True Heading | 0 | Mode-S | Calculated with declination when Magnetic Heading and Location are available |
| qnhs | Selected QNH | 2 | Mode-S | Actual value entered by the A/C crew |
| alts | Selected Altitude | 2 | Mode-S | Actual value entered by the A/C crew |
| hdgs | Selected Heading | 2 | Mode-S | Actual value entered by the A/C crew |
| altg | GNSS elipsoidal altitude (ft) | 0 | Mode-S | Either directly reported or from baro+difference |
| pic | Asterix PIC | 0 | Mode-S | EUROCONTROL-SPEC-0149-12 (ASTERIX Cat 021 Ed 2.4) Page 28 |
| tcm | ACAS/TCAS status | 0, alert only 2 | Mode-S | 0=not operational, 1=operational, 2=alert |
| ape | Autopilot engaged | 2 | Mode-S | |
| sil | ADS-B SIL | 1 | Mode-S | |
| sda | ADS-B SDA | 2 | Mode-S | |
| nacp | ADS-B NACp | 1 | Mode-S | |
| pest | Number of position estimations per second | MLAT | ||
| nocl | Number of sensors providing data aircraft | MLAT | ||
| tq | Time quality of this entry | Sensor | 0: GNSS 1: Sensor NTP 2: Server NTP |
| Value Origin | Description |
|---|---|
| <hex> | Derived from the ICAO ID or FLARM ID of the A/C |
| <src> | Value originates from the data source indicated in <src> field |
| DB | Value is read from database according to refrenced <hex> or <fli> value |
| Mode-S | Any Mode-S or ADS-B frame received from an A/C identified with <hex> field |
| FLARM | Any FLARM frame received from an A/C identified with FLARM ID equal to <hex> field |
Data Source Identifiers
"src", "ava" field contents
| src | Source | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| A | ADS-B | 1090 MHz + 978 MHz |
| M | Multilateration | 1090 MHz |
| L | OGN Decoder | 868 MHz |
| F | piAware | 1090 MHz |
| O | OGN Server Connection | 868 MHz |
| S | FLARM SkyLens FLARM | 868 MHz |
| D | FLARM SkyLens ADS-L | 868 MHz |
ADS-B Data Subclasses
"cla" field contents
| cla | Frequency | Shortcut | Source | Adress Type | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1090 MHz | Mode-S | Transponder | ICAO | |
| 1 | TISB_ModeA | TIS-B | Mode-A | ||
| 2 | TISB_Anonym | TIS-B | Anonymous | ||
| 3 | TISB_ICAO | TIS-B | ICAO | ||
| 4 | DF18_ADSR_ICAO | ADS-R | ICAO | ||
| 5 | DF18_ADSR_Anonym | ADS-R | Anonymous | ||
| 6 | DF18_NT_ICAO | Non transponder | ICAO | Obstacle or ground vehicle | |
| 7 | DF18_NT_Anonym | Non transponder | Anonymous | Obstacle or ground vehicle | |
| 8 | 978 MHz (UAT) |
UAT_ADSB_ICAO | Transponder | ICAO | |
| 9 | UAT_ADSB_Temporary | Transponder | Temporary | ||
| 10 | UAT_TISB_ICAO | TIS-B | ICAO | ||
| 11 | UAT_TISB_TrackID | TIS-B | Track-ID | ||
| 12 | UAT_SurfaceVehicle | Surface vehicle | FAA specific | ||
| 13 | UAT_FixedADSBBeacon | Surface vehicle | FAA specific | ||
| 14 | ISM (FLARM) | FLARM | Transponder | ICAO or FLARM non overlapping assignment |
FLARM only as soon as a Mode-S frame is received cla will change to 0 |
Aircraft categories
| Code | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | ADS-B | Light (< 15500 lbs) |
| A2 | ADS-B | Small (15500 >= lbs < 75000) |
| A3 | ADS-B | Large (75000 >= lbs < 300000) |
| A4 | ADS-B | Large (high vortex) |
| A5 | ADS-B | Heavy (>= 300000 lbs) |
| A6 | ADS-B | High performance |
| A7 | ADS-B | Rotorcraft |
| B1 | ADS-B | Glider/Sailplane |
| B2 | ADS-B | Lighter than air |
| B3 | ADS-B | Parachutist/Skydiver |
| B4 | ADS-B | Ultralight/Hang glider/Paraglider |
| B6 | ADS-B | UAV |
| B7 | ADS-B | Space/Trans-atmospheric vehicle |
| C1 | ADS-B | Surface vehicle - emergency |
| C2 | ADS-B | Surface vehicle - service |
| C3 | ADS-B | Obstacle - point |
| C4 | ADS-B | Obstacle - clustter |
| C5 | ADS-B | Obstacle - line |
| A0 | ADS-B | No category information |
| B0 | ADS-B | No category information |
| C0 | ADS-B | No category information |
| F0 | FLARM | None |
| F1 | FLARM | Glider/Motor glider |
| F2 | FLARM | Tow/Tug plane |
| F3 | FLARM | Helicopter/Rotorcraft |
| F4 | FLARM | Skydiver |
| F5 | FLARM | Skydiver/Drop plane |
| F6 | FLARM | Hang glider |
| F7 | FLARM | Paraglider |
| F8 | FLARM | Aircraft reciprocating |
| F9 | FLARM | Aircraft jet turboprop |
| F11 | FLARM | Balloon |
| F12 | FLARM | Airship |
| F13 | FLARM | UAV |
| F15 | FLARM | Static |
Raw Data Streaming to Network (TCP and UDP)
The binary and AVR raw data formats are identical to those of the Mode-S Beast and documented in Mode-S_Beast:Data_Output_Formats. For the Radarcape, there is one additional message that contains timestamp and FPGA configuration information, which is triggered by each 1PPS from the GPS module.
TCP or UDP port 10002
This is a CRC-checked mirror of the data as it comes from the FPGA, DF-11, DF-17 and DF-18 are CRC checked if enabled in FPGA. Includes Mode-A/C data with respect to the configuration setting.
TCP or UDP port 10003
Binary formatted raw data with all Modes-S data formats CRC-prechecked (eliminates transmission of the erroneous frames, reduces load on the network). All data from the FPGA is disassembled into messages and verified if correct.
TCP or UDP port 10004
Binary formatted raw data, pre-checked DF-11, DF-17 and DF-18 only: minimum load for the transmission path but contains most information. No Mode-A/C data.
TCP or UDP port 10005
Binary formatted raw data, only raw data frames of those aircraft where the location (latitude and longitude) is unknown. Used for special MLAT purposes. No Mode-A/C data.
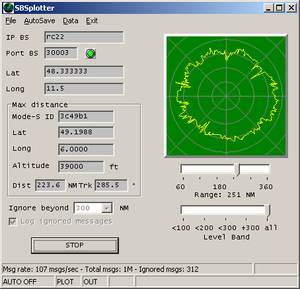
Port 30003 Service (TCP, UDP, and USB-serial)
Port 30003 style output (e.g., for use with SBS Plotter) can be provided without the need of an additional application on your PC.
The Radarcape provides this data stream on TCP port 30003, UDP port 30003, and the serial USB interface.
The format of the data output can be found in this document
The date in Port 30003 messages is always the Linux system date.
The timestamp instead is a GPS timestamp when the configuration is set to GPS timestamps and system time when the Radarcape operates in legacy 12 MHz time stamp mode.
Due to the low efficiency and high processor load caused by this protocol, please do not use Port 30003 unless really necessary.
A better way of getting the same data is the deltaDB service.
On Linux, a very simple method how to access the TCP stream of Port 30003 is socat:
socat - TCP:radarcape:80
Output of FLARM data on port 30003
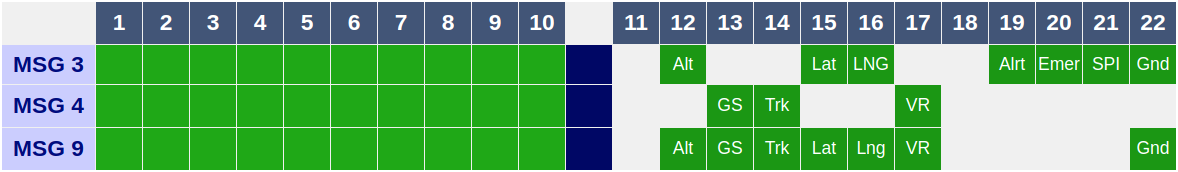
Starting with version 210406.1000.02, there is an option to also output FLARM frames on port 30003.
This can be configured on the web interface via Settings -> UDP Data Streaming Settings -> Port 30003 UDP Server -> Output Flarm data on Port 30003.
By default, there will be no FLARM data output on port 30003.
If enabled, FLARM data can be output using one of two options:
- FLARM data will be output using a
MSG,3message, which will be indistinguishable from aMSG,3message generated after reception of a Mode-S frame - FLARM data will be output using a newly introduced
MSG,9message, which contains only data received via FLARM
MSG,9 output format
The output format of the MSG,9 message is a combination the MSG,3 and MSG,4 messages.
MSG,9 messages contain all of the following fields in addition to the first ten common fields: Altitude, Ground Speed, Track, Latitude, Longitude, Vertical Rate and IsOnGround.
These messages will only be generated if enabled in the settings menu and will only contain data received via a local FLARM receiver.
USB Serial Port Data Access
While some features existed before, this feature is more reliable on Debian 10 . See Linux Distribution Versions History.
The device supports one selectable data stream out of following sources on a virtual serial port via the back side USB port:
- Raw FGPA data - including Mode-A/C data
- CRC pre-checked Mode-S with Mode-A/C data
- Mode-S Frame types DF-11, DF-17 and DF-18 only
- Mode-S Frames of all aircraft without a known location
- Port 30003 format
The output can be selected in the configuration menu. Due to processor load, it is recommended to keep this feature disabled when not required.
The setting can be changed on the fly and will apply without the need to reboot the device.
Note: On the Radarcape of 1st Generation two serial ports appear on the USB interface. One of them is a hardware serial port for debug
Note: When powering on, the external +5 V power supply MUST be connected prior to connecting the USB cable
The serial port uses a standard USB class driver and should install automatically in any Operating System that is currently supported.